publications
publications by categories in reversed chronological order. generated by jekyll-scholar.
2024
-
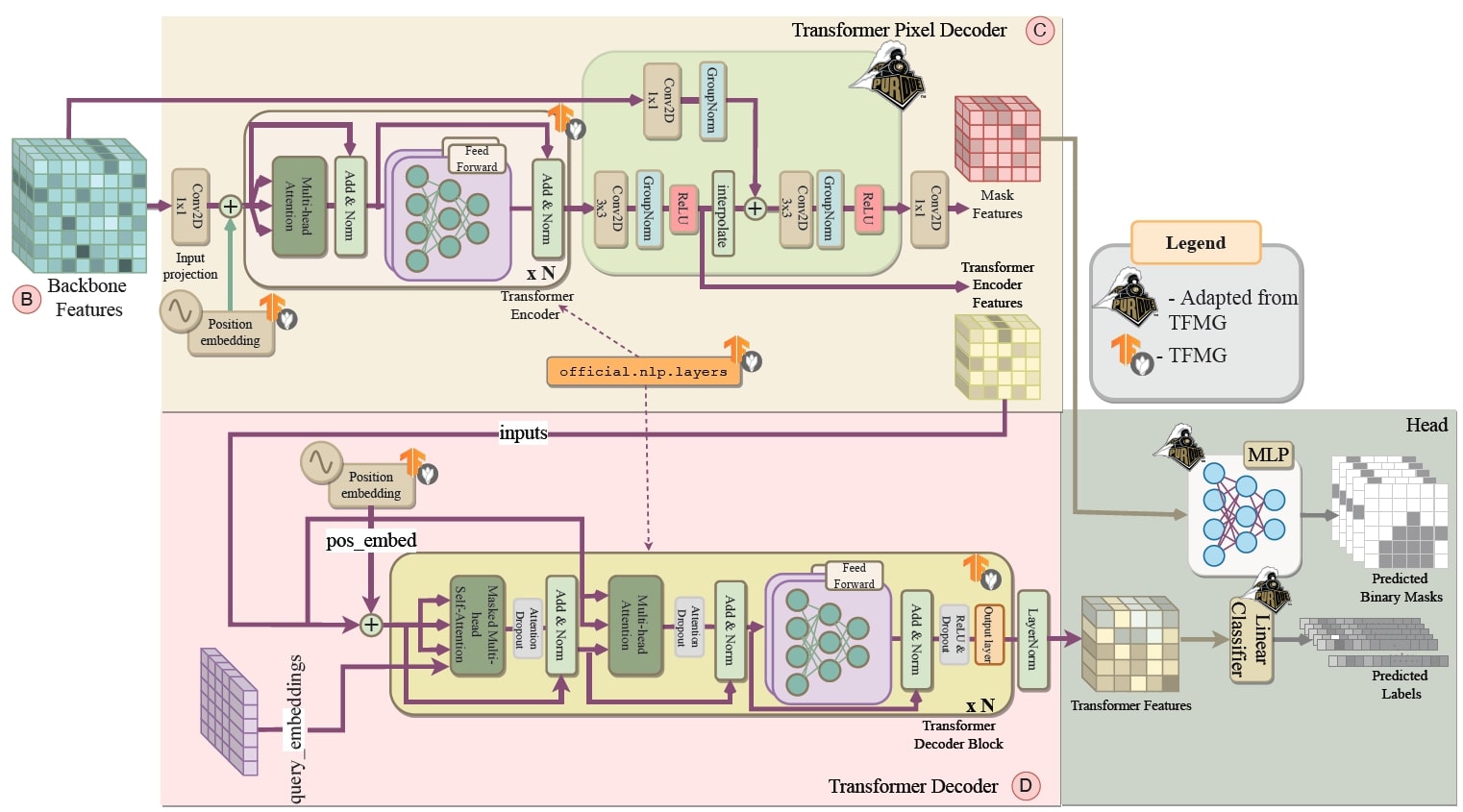 A Partial Replication of MaskFormer in TensorFlow on TPUs for the TensorFlow Model GardenVishal Purohit , Wenxin Jiang , Akshath R. Ravikiran , and 1 more authorarXiv preprint, arXiv:2404.18801, Apr 2024
A Partial Replication of MaskFormer in TensorFlow on TPUs for the TensorFlow Model GardenVishal Purohit , Wenxin Jiang , Akshath R. Ravikiran , and 1 more authorarXiv preprint, arXiv:2404.18801, Apr 2024This paper undertakes the task of replicating the MaskFormer model a universal image segmentation model originally developed using the PyTorch framework, within the TensorFlow ecosystem, specifically optimized for execution on Tensor Processing Units (TPUs). Our implementation exploits the modular constructs available within the TensorFlow Model Garden (TFMG), encompassing elements such as the data loader, training orchestrator, and various architectural components, tailored and adapted to meet the specifications of the MaskFormer model. We address key challenges encountered during the replication, non-convergence issues, slow training, adaptation of loss functions, and the integration of TPU-specific functionalities. We verify our reproduced implementation and present qualitative results on the COCO dataset. Although our implementation meets some of the objectives for end-to-end reproducibility, we encountered challenges in replicating the PyTorch version of MaskFormer in TensorFlow.
2023
-
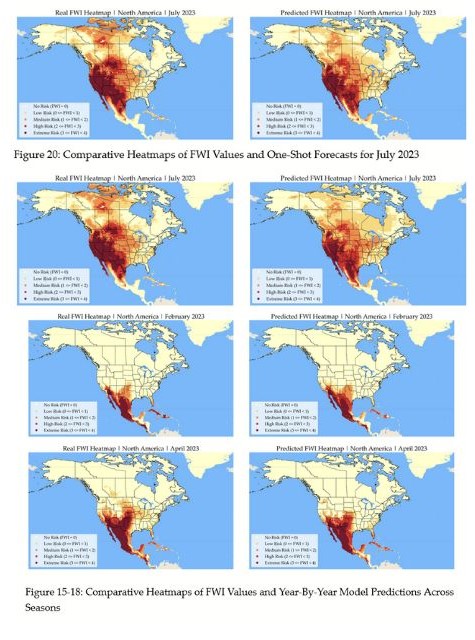 Time-Driven Fire Risk Forecasting: Leveraging Historical Trends for Enhanced Seasonal ModelingRoma Jain , Akshath R. Ravikiran , and Pareekshith KattiMay 2023
Time-Driven Fire Risk Forecasting: Leveraging Historical Trends for Enhanced Seasonal ModelingRoma Jain , Akshath R. Ravikiran , and Pareekshith KattiMay 2023Wildfires pose severe threats across North America, causing extensive damage to lives, ecosystems, and property. To address this, accurate fire prediction and forecast outlooks are crucial for effective mitigation. Agencies like the National Interagency Fire Center (NIFC) and the Canadian Wildland Fire Information System (CWFIS) provide vital fire risk assessments. In this paper, our main goal was to demonstrate the sufficiency of historical fire risk data for accurate forecasting. We focused on weather-calculation-based fire risk prediction models, specifically exploring the temporal aspect’s importance in enhancing accuracy. Two encoding methods, One-Shot and Year-By-Year, used for encoding the seasonal changes of fire weather, were analyzed for their implications in fire risk assessment, revealing contrasting attributes. The One-Shot model shows superior accuracy and favorable plots, while the Year-By-Year model offers alternative insights. Despite minor differences in feature importance between the two models, both effectively utilized historical fire weather data for forecasting. This study contributes significantly to fire risk prediction by providing a comprehensive analysis of temporal influences and the effectiveness of different encoding methods. The findings guide model design improvements, bolstering wildfire management and protection measures.